This page includes the main information on aromatic isocyanates more precisely the Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) and the Dihenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI) Their physical characteristics, their effects on health, the means to detect them (aromatic gas detector (aromatic isocyanate) as well as adapted respiratory protection equipment (gas mask or a ventilation device with Combined Filter Type E-P2).
The Aromatic isocyanates Today serve the synthesis of polyurethanes. The Toluene diisocyanate Also called TDI is used mainly in the manufacture of soft padding foams. The Dihenylmethane diisocyanate also called MDI It is useful in the production of rigid foams used for insulation and can also be used as a binder in foundries.
The TDI (toluene diisocyanate) is in the form of a colorless or pale yellow liquid with a detectable penetrating and penetrating odor at low concentrations (of the order of 1 to 2 ppm). The 4,4'-mdi (diphenylmethane diisocyanate) is in the form of white or yellow crystals pale moldy light smell.
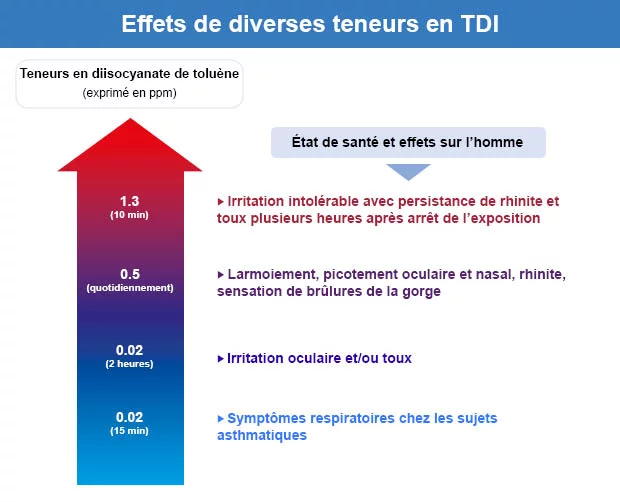
Acute exposure to TDI and MDI isocyanates causes lesions of respiratory mucosa that can be serious. Irritation of the skin and eyes can also be particularly important. Chronic exposure to TDI can cause professional asthma, as well as an accelerated decline in respiratory function. The repeated exposure to MDI translates into allergic events: eczema, asthma, hypersensitivity pneumopathy, conjunctivitis.
After short exposure but with high concentrations, MDI may cause reactions that may appear only after a few hours: mucosal irritation (conjunctivitis, rhinitis, pharyngitis, nausea, vomiting), Skin irritation, pulmonary irritation (chest pain, cough ...), neurological disorders (vertigo, balance and conscience disorders, headaches) and in the most serious cases of pulmonary edema.
In case of repeated exposures at low concentrations of MDI, it may appear reactions a few weeks for several years after: contact eczema, allergic asthma or pneumonic hypersensitivity pneumonium.
Few equipment is available for Detect aromatic isocyanates : Liabilitary passive badges to be carried by employees or a much more complex (expensive) optical gas analysis device.
Isocyanates being very irritating to the eyes as for the airways, we will focus on a full mask For short-term interventions or in low gas concentration or attended (more comfortable) ventilation device with Combined Filters A2B2-P3 for the TDI or A-P3 for the MDI. In case of emergency interventions, an insulating respiratory apparatus will be imperative.
check_circle
check_circle
Nous utilisons des cookies tiers pour améliorer votre expérience de navigation, analyser le trafic du site et personnaliser le contenu et les publicités. En savoir plus