In the chemical, oil and food industries, many dangerous substances in the form of gases, fumes, liquids, powders or dusts are used or released during the manufacture, processing or storage of common products such as: gases, hydrocarbons, plastics, varnishes, paints, medicines, powders, cereals, cosmetics, glues, etc.
Conditions for an explosion to occur
An explosion can occur when 3 elements come together:
This is the lowest energy that is required to initiate ignition of the most readily flammable explosive atmosphere under specified test conditions.

There are many sources of ignition that can cause an explosion:
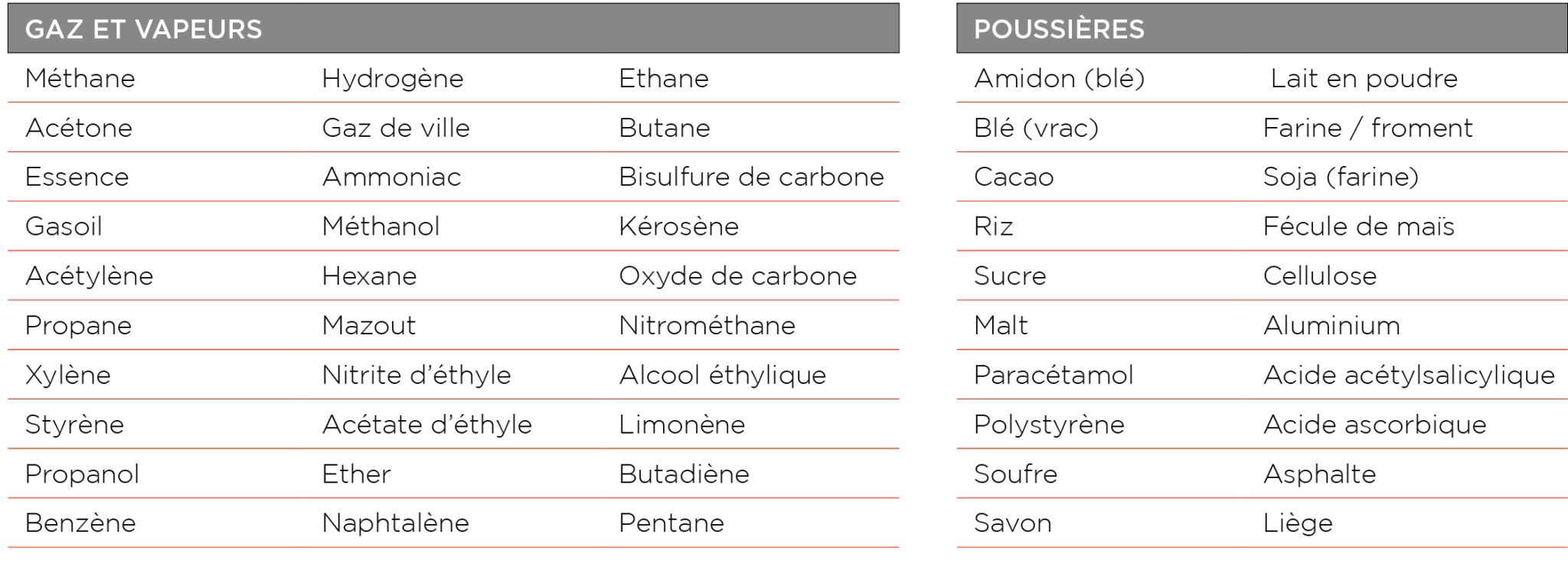
They are divided into two main categories: flammable gases, vapors and liquids on the one hand, and dust layers or particle clouds on the other.
The table below gives a non-exhaustive overview of the most common substances:
check_circle
check_circle
Nous utilisons des cookies tiers pour améliorer votre expérience de navigation, analyser le trafic du site et personnaliser le contenu et les publicités. En savoir plus